Challenge: Optimize 20-Year Bridge Improvement Programs
With increasing challenges of ageing and deterioration of bridges, climbing maintenance backlogs, and insufficient investments, optimization of long-range bridge improvement programs has been a high priority for Iowa DOT. Bridge programming decisions need to focus on optimizing budget allocation and investment strategies to meet organizational objectives and performance metrics. Programs need to be designed to ensure the safety and adequacy of managed bridge inventories, reduce risks and lifecycle costs, and maximize return on investment. Iowa DOT required a unique solution that can support detailed analysis of the relationship between funding levels and performance and risk measures of the bridge inventory, and the ability to optimize project selections to ensure that scarce funding resources are invested on the right project at the right time.
“IDS software helped show us the impact of differing funding levels. This helped us understand the daunting task ahead of us. The system’s ability to show how funding levels change the overall condition of the bridge population is very beneficial. This system provided information that quantified how much spending was needed to better preserve our bridge population. The system verified spending levels that we knew were needed, but were only able to use broad assumptions to determine ourselves. Being able to see how the health of the bridge population changes with different spending levels is something that has always been difficult to quantify.”
– Scott Neubauer, Iowa DOT
Solution: Asset Optimizer
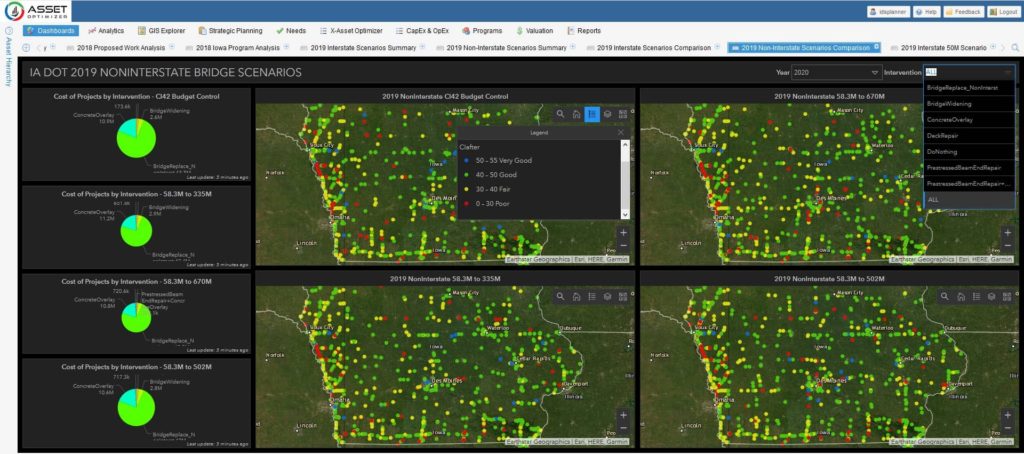
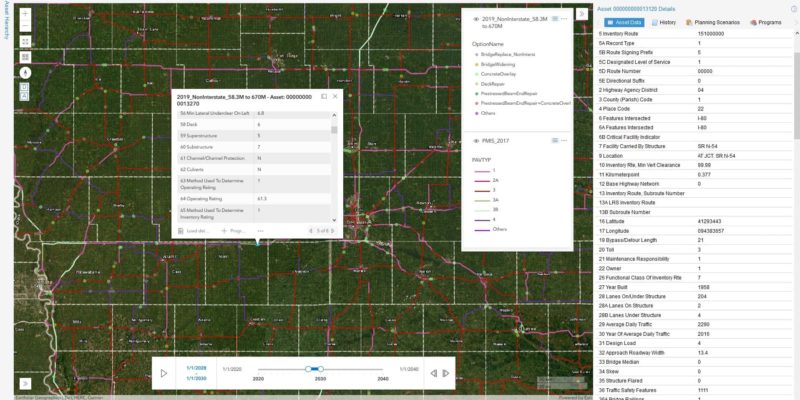
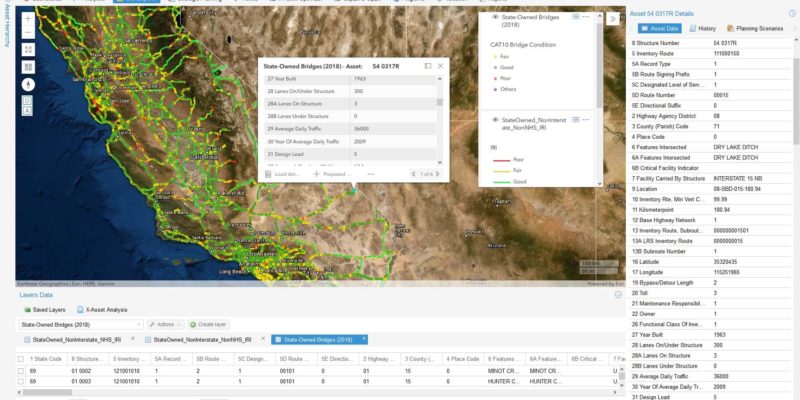
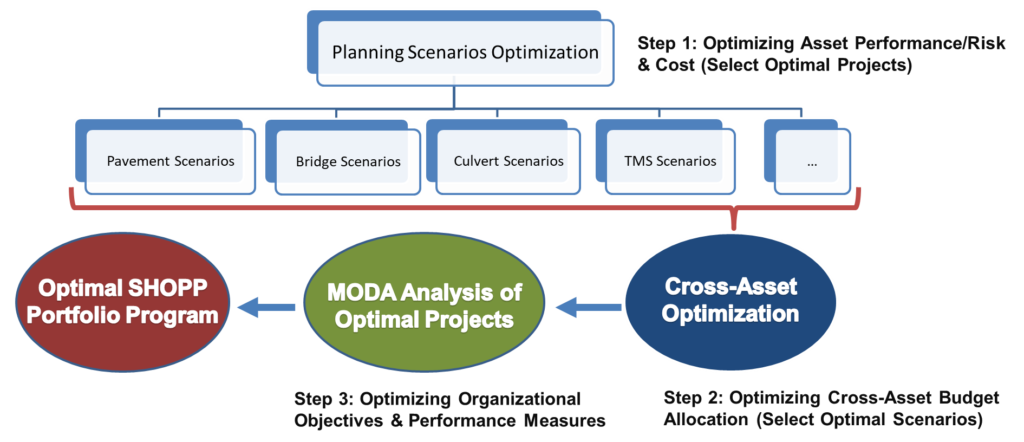
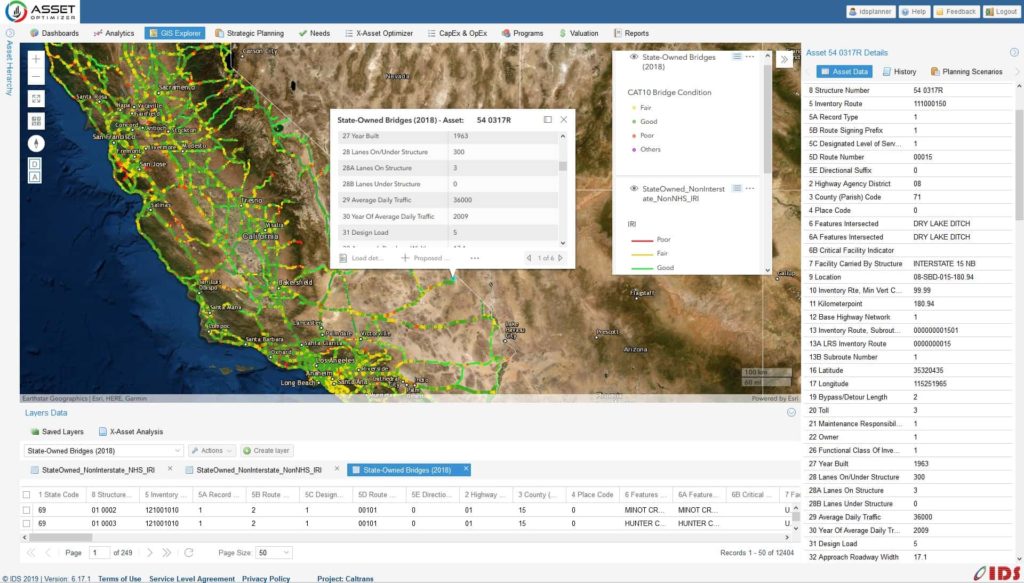
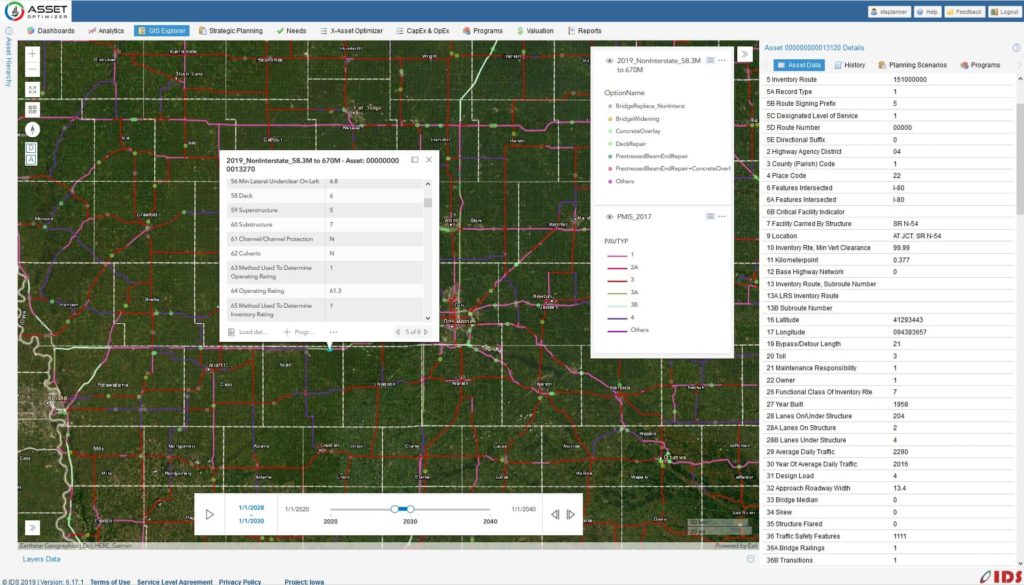
Asset OptimizerTM GIS-centered cloud-based software was used to perform in-depth data analysis and develop optimal 20-year risk-based plans for Iowa state-owned bridges. The software implemented a unique risk model, developed by Iowa DOT engineers, to assess the priority of bridges based on structural condition and load rating, as well as a range of criticality factors, e.g., vertical and horizontal clearances, traffic levels, type of carried roadway, detour length, and waterway adequacy. Data-driven deterioration and risk models were developed based on historical NBI data and considered a range of variables such as age, traffic volume, design load, and deck type, etc. Cost and benefits models for various bridge improvement actions were defined, along with various constraints governing these actions.
Multiple planning scenarios were defined for interstate and non-interstate bridge groups. Iowa DOT engineers defined scenario parameters including budget profile, target condition or risk metrics, budget splitting among improvement methods, average annual inflation rate, etc. Asset OptimizerTM generated optimal project lists that satisfied all defined criteria and constraints. Scenario analysis helped to quantify relationships between funding levels and system condition and risk metrics, and to develop optimized and defensible long-range bridge improvement program.